
Manufacturing and industrial facilities are operating in ways they scarcely could have imagined a few decades ago. Greater connectivity and information sharing is significantly transforming companies and their operations. They are converging IT and operations technology (OT) systems and using new technologies such as mobile, analytics, cloud and virtualisation to do more than ever before.
However, just as the nature of manufacturing and industrial operations has changed, so have the security risks. More connected operations can create more potential entrance points for security threats. These threats can come in many different forms – physical or digital, internal or external, malicious or unintentional.
As a result, industrial security must be holistic. It should extend from the enterprise through the plant level and even out to end devices, and address risks across people, processes and technologies. It should also involve collaboration between IT and OT personnel. Both sides have vital roles to play.
An holistic approach
Three key elements of an holistic approach to security include:
1. Security assessment: conduct a facility-wide assessment to understand risk areas and potential threats.
2. Defence-in-depth approach: deploy a multi-layered security approach that establishes multiple fronts and tiers of defence.
3. Trusted vendors: verify that automation vendors follow core security principles when designing their products.
Security assessment
Developing and implementing an effective industrial security programme requires that users first understand the risks and areas of vulnerability that exist within an organisation.
A security assessment will help to understand the current security posture regarding software, networks, control system, policies and procedures, and even employee behaviours. It should be the starting point for any security policy. At a minimum, a security assessment should include the following:
• An inventory of authorised and unauthorised devices and software.
• Detailed observation and documentation of system performance.
• Identification of tolerance thresholds and risk/vulnerability indications.
• Prioritisation of each vulnerability based on impact and exploitation potential.
The final outcome of any security assessment should include a documented and actionable list of mitigation techniques required to bring an operation to an acceptable risk state.
Defence-in-depth security
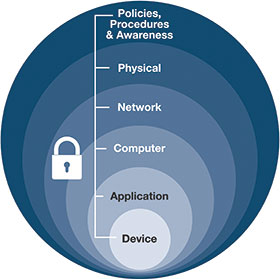
Industrial security is best implemented as a complete system across operations, and a defence-in-depth (DiD) security framework supports this approach. Based on the notion that any one point of protection can and likely will be defeated or breached, DiD security establishes multiple layers of protection through a combination of physical, electronic and procedural safeguards.
A DiD security approach consists of six main components including: defined policies and procedures, physical security, network infrastructure, computer/software, application, and device authentication and identification.
Trusted vendors
Automation vendors are just as integral to helping you meet security goals as they are to production, quality and safety goals. Before selecting vendors, request they disclose their security policies and practices. Consider if they follow five core security principles for designing products used in a control system. These include:
• A secure network infrastructure: vendors can help keep information in the automation layer secure and confidential. For example, embedded technology can validate and authenticate devices before they are granted access to a network.
• Authentication and policy management: company policies dictate data access levels for employees. Automation products can support these policies using access control lists to manage user access to devices and applications.
• Content protection: intellectual property is the lifeblood of operations. Automation solutions can help protect it by assigning passwords to routines and add-on instructions, and by using digital rights management to limit users’ ability to view and edit device data.
• Tamper detection: built-in tamper detection can detect any unauthorised system activity and alert the right personnel. It also can log key details, such as where the attempted intrusion took place, how it occurred and if anything was modified.
• Robustness: a robust vendor security approach includes providing security training to employees, using design-for-security development practices, and testing products to global security standards. It also includes conducting final security reviews before products are released, verifying processes stay current with standards and technologies, and having a plan in place to address vulnerabilities.
Monitor and evolve
Security threats are not relenting. They will only continue to evolve as the industry changes its security practices or implements new defences. A good risk management strategy must keep pace, and should be ongoing, and evolve with or ahead of the changing threat landscape.
With the continual evolution of operations toward greater connectivity, the vastness of today’s security concerns can be daunting. The approaches outlined here can help align the company with best industry practices for protecting intellectual property, facilities, assets, employees and competitive advantages.
For more information contact Christo Buys, Rockwell Automation, +27 (0)11 654 9700, [email protected], www.rockwellautomation.co.za
| Tel: | +27 11 998 1000 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.rockwellautomation.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Rockwell Automation |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved