
Now, more than ever, capital and operational cost can be reduced while enhancing operational safety and increasing production uptime by applying transformative methods such as Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modelling.
ProRisk is a specialised operational risk consultancy under the ProGroup of companies. Over the past decade, ProRisk has developed a robust suite of services including:
• Process Hazard Analysis (PHA).
• Critical Control Management.
• Consequence Modelling.
• Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA).
Operating across the Middle East and sub-Saharan Africa, ProRisk brings deep technical expertise and a commitment to data-driven safety. The company’s mission is clear: to remove uncertainty from operational risk and deliver pragmatic, cost-effective safety solutions.
Introduction to operational risk
In today’s industrial landscape, organisations face mounting pressure to optimise operational efficiency while maintaining high safety standards and reducing both capital and operational expenditure. One of the most effective strategies to achieve these objectives is the application of transformative methods, such as Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modelling, to inform the design and placement of fire and gas detection systems.
According to process safety specialist at ProRisk, Guillaume De Swardt, operational risk in high-hazard industries refers to the potential for significant losses of hazardous substances arising from failures in internal processes, personnel or external events. These risks span a wide range of exposures and may lead to severe consequences, including health and safety impacts, financial loss, reputational damage, legal liabilities and regulatory non-compliance.
ProRisk provides services to high-hazard industries such as petrochemical plants, mining operations, energy facilities and gas liquefaction and storage terminals. The company’s objective in operational risk engineering is to proactively identify hazards and reduce associated risks by implementing robust preventive and mitigative controls.
Fire and gas safety systems informed by risk-based modelling
Industrial environments are frequently exposed to hazardous materials such as flammable and toxic gases and liquids. When loss of containment occurs, effective fire and gas detection is critical to mitigate the severity of such incidents. The effectiveness of these detection systems depends heavily on optimal detector placement and appropriate device specification. ProRisk promotes a Risk-Based Assessment Methodology aligned with the following standards and guidelines:
• ISA-TR84.00.07: Guidance on the Evaluation of Fire, Combustible Gas, and Toxic Gas System Effectivenes.
• BS 60080: Guidance on the Placement of Permanently Installed Flame and Gas Detection Devices.
This approach incorporates detailed facility-specific inputs such as process conditions, three-dimensional (3D) plant geometry, published failure data and historical meteorological information to perform consequence and risk exceedance modelling. This method offers significantly greater accuracy than traditional conservative techniques by reducing reliance on coarse assumptions.
The Risk-Based Assessment Methodology, in addition to detector placement optimisation, can also inform equipment layout and provide input to exclusion zone definition. The following examples illustrate these additional benefits:
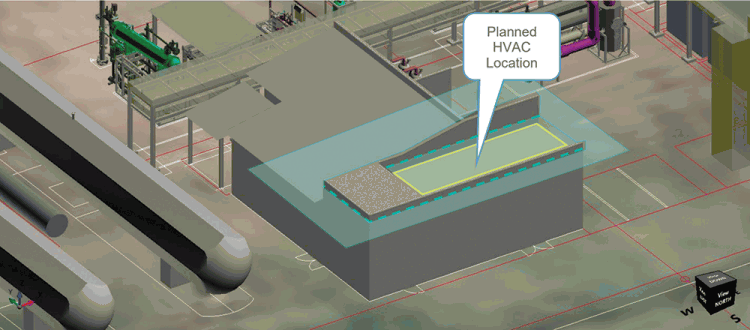
Optimising HVAC intake location at a CO2 capture facility
At a new CO2 liquefaction facility, a risk assessment was conducted to determine the optimal HVAC intake location
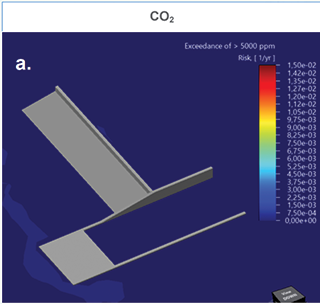
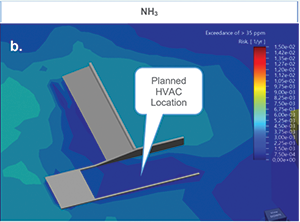
CFD-based modelling was used to assess the risk of exceeding toxic exposure thresholds. Results confirmed that the selected intake elevation (5,3 m) had negligible CO2 risk (see Figure 1a) and a low-probability NH3 exceedance of 35 ppm at a frequency of 1-in-1000 years (see Figure 1b), validating the design. In Figures 1a and 1b, the darker the plot colour, the lower the risk of asphyxiation and toxic exposure.
Furthermore, the same modelling informed a 50% reduction in planned gas detectors while maintaining the detection coverage criteria, thereby demonstrating both safety enhancement and cost efficiency.
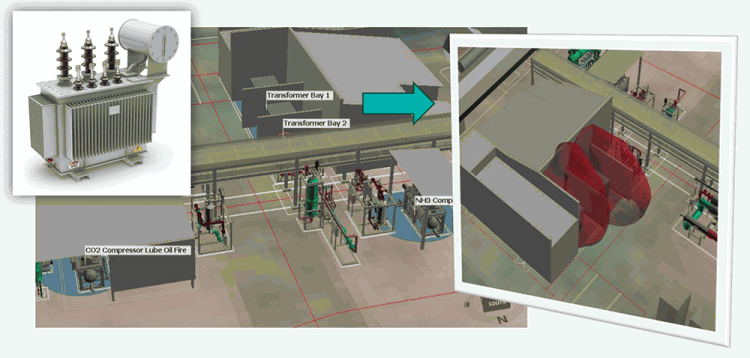
Pool fire modelling in transformers and compressors
Transformer failures and compressor lubrication oil system malfunctions pose serious fire risks due to combustible oil releases, potentially leading to fire escalation events and impacting emergency escape routes and adjacent structures and equipment.
CFD modelling can be applied to assess thermal radiation exposure from pool fires and its impact on personnel escape routes and adjacent equipment.
By applying risk-based pool fire modelling at the aforementioned CO2 liquefaction facility, detector placement was strategically optimised using historical wind data and the site’s specific geometric constraints. “This approach enabled accurate coverage, facilitating early fire detection and reducing the risk of personnel exposure and damage to adjacent equipment from radiation levels exceeding critical thresholds,” explains De Swardt.
Flammable gas dispersion in a bulk fuel storage facility
A risk assessment was undertaken for a bulk fuel storage site near a national roadway. The goal was to assess and optimise flammable gas detector coverage for a tank overfill scenario. A transient CFD simulation determined that in the worst-case event, a flammable vapour cloud would reach the adjacent roadway within seven minutes of detection − far below the standard emergency response window of 15 to 30 minutes.
Based on this finding it was recommended that the system’s executive action logic be set to one-out-of-N (1ooN) detection enabling immediate shutdown and response, as opposed to the typical 2ooN setting which might delay critical actions.
De Swardt mentioned that this transient gas dispersion analysis enabled the site leadership to make data-driven emergency response decisions.
Future outlook: Leveraging digital twins for real-time risk management
A digital twin, comprising real-time data feeds, simulation analytics and 3D visualisation provides a live, dynamic model of facility operations. In one instance, a client operating an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) plant experienced a highly toxic gas release. Due to uncertainty regarding the dispersion and impact area the entire facility was evacuated, resulting in costly downtime.
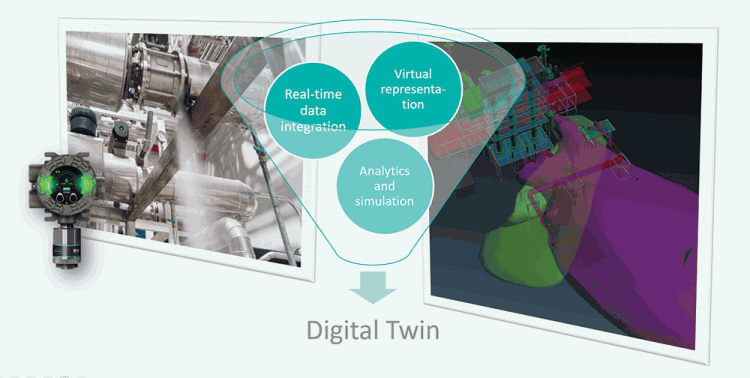
Had a digital twin been available the impact zone could have been evaluated in real time, enabling targeted evacuations and continued safe operations in unaffected areas. This exemplifies the potential of digital twins to dramatically enhance decision-making, improve response times and minimise operational disruption.
“With a commitment to removing the guesswork from operational risk, we are exploring the application of digital twin technology in the operational risk environment, ensuring we remain at the forefront of technological advancements,” concludes De Swardt.
For more information contact ProRisk,

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved