Overload protection
September 2008
Electrical Power & Protection
Circuit breaker technologies.
Each component of an electrical installation is designed for use at a particular rated current. When the component is used within the designed current limit it will have a specific service life expectancy, which is the length of time for which the insulation will remain operationally safe.
When a component is overloaded, the temperature in the insulation exceeds the design limit, the insulation begins to deteriorate and the service life will be reduced. Quantitatively, this deterioration depends on both the temperature rise and time for which the insulation is exposed to the overload. Precautions should be taken to avoid, or at least reduce to a minimum, overloading of electrical components. An overload condition can be detected by monitoring the current flowing into an item of equipment and the time for which it flows.
The method of overload sensing incorporated into circuit breakers is usually achieved through one of three different technologies:
* Solid-state electronic sensing.
* Thermal-magnetic sensing.
* Hydraulic-magnetic sensing.
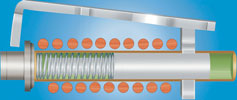
Hydraulic-magnetic mechanism as current increases
Solid state electronic sensing
This technology is often combined with microprocessor controllers and is generally restricted to larger frame circuit breakers due to cost considerations.
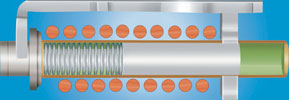
Hydraulic-magnetic mechanism showing trip bar activated
Thermal sensing
This is the oldest technology and has been used since the first appearance of miniature and moulded case circuit breakers. Thermal sensing components such as bimetals, are supported by instantaneously operated magnetic trips for short circuit protection.
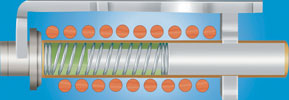
Hydraulic-magnetic mechanism remains latched after trip
Hydraulic-magnetic sensing
This technology is widely used in South Africa and eliminates the inconvenience of early tripping of thermally operated circuit breakers at elevated ambient temperatures. Hydraulic-magnetic circuit breakers have the advantage of more accurate calibration of tripping curves and make possible a variety of tripping curves to suit application-specific requirements including fractional ampere ratings.
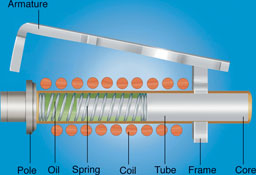
Hydraulic-magnetic circuit breakers operate on the principle of the opposing forces of a spring and a viscous fluid controlling the magnetic attraction on a ferrous piston inside a non-magnetic cylinder. The design has both a time delay operation (overload trip) and an instantaneous operation in the case of a short circuit.
Hydraulic-magnetic mechanism at low current
When an overcurrent occurs, the magnetic force produced in the coil overcomes the core spring and the core moves towards the pole piece. The closer the core gets to the pole piece, the more magnetised the pole piece becomes. This attracts the armature, which in turn actuates the trip bar. The viscosity of the fluid and the characteristics of the spring govern the time delay. If the overcurrent is excessive, the magnetic field is such that the armature is immediately attracted to the pole piece without the influence of the core.
For more information contact CBI-electric: low voltage, +27 (0)11 928 2000, [email protected], www.cbi-electric.com
Further reading:
South African businesses can alleviate energy price crisis
Electrical Power & Protection
While grid instability remains a concern, the immediate and most critical driver of South African commercial and industrial investment in renewable energy is the escalating cost of electricity.
Read more...
Real-time modelling is the key to a resilient, bi-directional energy grid
Schneider Electric South Africa
Electrical Power & Protection
Utilities and municipalities are facing a challenge as the country’s legacy power grid, engineered for one-way energy delivery from centralised suppliers to end-users, must rapidly evolve to meet a new paradigm.
Read more...
Shielding data centre growth from the looming power crunch
Schneider Electric South Africa
Electrical Power & Protection
Today’s digital economy is placing unprecedented strain on the power grid. The good news is that these challenges are not insurmountable. By adopting proactive strategies such as alternative power sources, infrastructure planning and software, operators can secure capacity, build resilient facilities and scale sustainably.
Read more...
Circuit breaker innovations
Schneider Electric South Africa
Electrical Power & Protection
Recent advancements in circuit breaker technology have seen a major step forward in setting new standards for efficiency and sustainability in data centres, industrial and commercial infrastructure.
Read more...
Common battery tester errors and what they mean
Comtest
Electrical Power & Protection
Battery testers help quickly assess battery health, diagnose issues, and determine whether a battery needs a charge or replacement. This guide covers some of the most common battery tester errors, what they mean, and what can cause them.
Read more...
Cathodic protection design considerations that influence ESG outcomes
Omniflex Remote Monitoring Specialists
Electrical Power & Protection
Major infrastructure like wharves, bridges, pipelines and tanks are at constant risk of corrosion. David Celine, managing director of cathodic protection specialist Omniflex, explains how CP system design can support ESG commitments, while simultaneously lowering costs and improving maintenance capabilities.
Read more...
Africa’s digital future – building critical power infrastructure for data centre leadership
Electrical Power & Protection
Africa’s digital economy is growing rapidly, and countries like South Africa, Nigeria and Kenya are leading the way. However, a major challenge remains. Sustainable and reliable power systems must form the backbone of Africa’s digital growth to ensure lasting success.
Read more...
Recovering condensate and waste heat
Electrical Power & Protection
According to Associated Energy Services, strong partnerships with thermal energy users optimise opportunities to benefit from condensate return. waste heat recovery and the prevention of system contamination.
Read more...
Quantum engine powered by particle entanglement
Electrical Power & Protection
In a landmark achievement that signals a new era in energy research, a team of physicists in China has carried out the first successful test of a quantum engine powered by particle entanglement. This technological breakthrough represents a fundamental shift in our approach to energy production.
Read more...
Advancing sustainability in South Africa’s fruit industry
Schneider Electric South Africa
Electrical Power & Protection
Schneider Electric, together with Technoserve Medium Voltage, has implemented its advanced SF6-free MV switchgear at Two-a-Day situated in Grabouw in the Overberg district.
Read more...