
Around the world regulatory bodies and consumers are demanding ever increasing levels of traceability from agri-businesses, the food supply chain and pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Programs such as the €12m, 5-year European Commission funded TRACE project1, which came to an end in 2010 bear witness to the fact that significant investment is being made in this area.
TRACE was tasked to look at traceability from two perspectives:
* Internal traceability: The ability to trace product information internally in an organisation.
* Chain traceability: The ability to trace product information through the links in the supply chain.

Motivation
Under EU legislation 'Food producers' includes animal feed producers where animals are destined for human consumption. Under US legislation it even extends to include pet food manufacturers.
There are many motivators for food producers to incorporate traceability into their operations:
* Regulatory compliance: Since 1 January 2005 food producers in the EU have been required to comply with Regulation 178/20022 which mandates traceability. After '9/11' food traceability legislation in the USA became more stringent with the introduction of the Bioterrorism Act of 20024.
* Consumers are more informed: As the media broadcast news of food scares (think Glycol in Italian wine, hydrocarbons in mineral water, carcinogenic red dye in your favourite chilli powder...), consumers are demanding information about what is in their food and where it comes from.
* Recall prevention: Traceability systems can help to prevent out-of-specification product from leaving the manufacturing plant.
* Targeted recalls: When things do go wrong, functional traceability facilitates recalling only specific production lot numbers rather than all product manufactured over some period. Targeted recall limits direct cost of recall and reputational cost.
* Premium pricing: There are consumers who will pay a premium to know that their potatoes are really grown organically or that their coffee comes from a 'fair trade' supplier. The credentials of these premium products can only be established by having a credible, documented and auditable genealogy.
* Other: The spin off from improved traceability monitoring often results in economic benefits in production yield, stock rotation and distribution logistics, along with improved knowledge of inventory and manufactured cost – these aspects become more visible through monitoring required to comply with traceability.
A 2008 AMR Research study5 found that out of a sample of 251 food producers polled for the study revealed that more than 40% of the respondents that had had a recall in the previous year had experienced losses of US$20m or more on preventable product recalls.
Material receiving
For material receiving, the link between chain traceability and internal traceability takes place at the receiving dock of a manufacturing plant.
Since most manufacturers receive raw materials from many different suppliers, each of which will have their own lot/batch numbering methodology the manufacturer needs to:
* Capture supplier information: This is typically obtained from the Approved supplier database and includes:
- Supplier name
- Supplier contact details
- Supplier reference (supplier delivery note)
- Quantity and unit of measure (UOM) per delivery note
* Capture shipper information
- Serial Shipping Container Code
- Plant of origin
- Zone of origin
- Delivery vehicle registration
- Deliverer details (person delivering)
* Capture purchaser order transaction information:
- Purchase order number
- Order quantity
- Order UOM
- Item code of ordered item
- Item description of ordered item
- Purchaser name
* Capture purchaser receipt transaction information:
- Goods Receipt reference (GRN)
- Receiver details (person receiving)
- Destination location (warehouse/bin number)
* Capture material information
- Supplier lot number
- Certificate of Analysis (COA) reference
- Manufactured date
- Expiry date
* Allocate an Internal Lot Number that is in accordance with the manufacturer’s own lot/batch numbering methodology.
* Record the actual quantity and UOM counted.
* Label the materials with human and machine readable markings to facilitate subsequent barcode scanning.
* Sample according to sampling regime for the particular material and generate the necessary sample labels.
The typical data that needs to be collected is illustrated in Figures 1 through 4, with a summary of the data receipt shown in Figure 5.
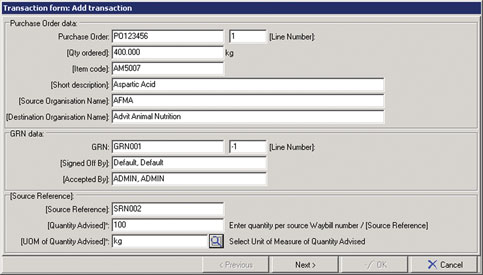
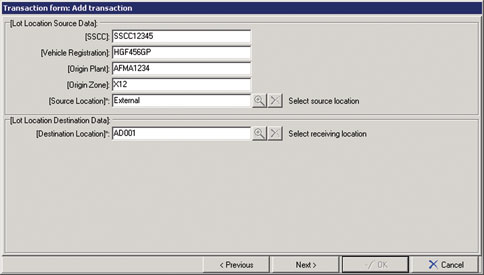
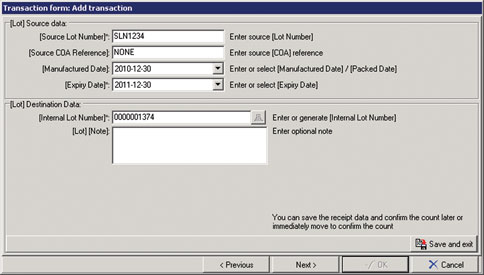
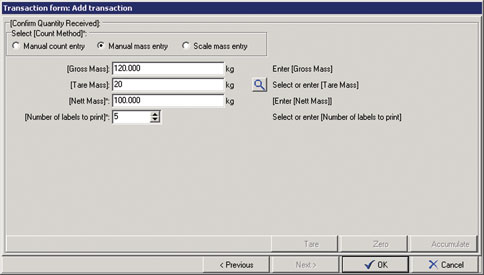
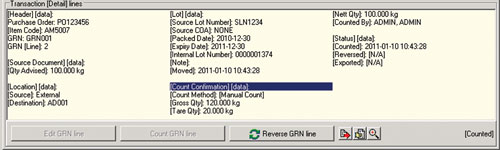
Internal traceability
Internal traceability starts at the receiving dock of a manufacturing plant as described above. The goal should be to ensure that only correctly labelled and QA released material is moved outside the quarantined receiving area.
Material traceability within typical manufacturing processes is often associated with batch processes and formulation. Manufacturers need efficient ways of associating identifiable batches of finished product with the separate lot numbers of raw material or semi-manufactured material that make up the final composition.
Formulation management software is able to capture in real-time the quantities of material consumed (based on feedback from electronic scales, loadcells or flowmeters) and the lot numbers of raw material consumption based on scanning the bar-coded lot number of the raw material. This eliminates the need for error-prone manual capture of lot numbers on batch sheets.
Consumption data includes:
* Header information of the Control Recipe.
* Details of the Control Recipe phase and step against which the material was consumed.
* Target mass and UOM.
* Tare mass and UOM.
* Actual mass and UOM.
* Material ID, Name and Lot number of material consumed.
* ID of the device (scale/flowmeter serial number) that recorded the consumption.
* Date and time of consumption.
* ID of user responsible for the process.
Figure 6 shows a typical operator view of a Control Recipe bill of materials (BOM) where one ingredient addition step has been completed.
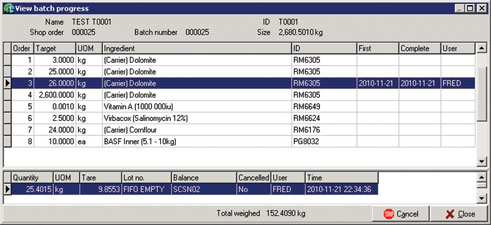
Chain traceability
Regulations such as EC178/2002 and the US Bioterrorism Act are based on the premise full traceability from first point of origin (eg, the farm) to final point of sale (eg, the retail store) is achievable if each organisation has full knowledge of:
* The immediate upstream supplier and transporter (the Immediate Prior Source or IPS).
* Internal traceability.
* The immediate downstream customer and transporter (the immediate subsequent recipient or ISR).
Although this is easily achieved by applying the practices described above at points of receipt, dispatch and internally, a study by the US FDA found that out of 40 'fork to farm' audits, only five had unbroken traceability chains.
XML to the rescue?
One of the reasons for these broken traceability chains is the sheer volume of data that needs to be passed between each participant in the chain and the disparate systems that each manufacturer and logistics business has in place.
If there is no standardised data interface between these traceability partners then manual data capture is almost certain to lead to broken chains.
The TRACE initiative has developed TraceCore XML to address this while on the other side of the Atlantic ISA95 and WBF, the Organization for Production Technology have been addressing these issues with the ongoing development and refining of B2MML (Business To Manufacturing Markup Language) and BatchML (Batch Markup Language).
We can look forward to a time when these two initiatives can be consolidated to form a single international standard supporting both Internal and Chain traceability.
Glossary
Traceability: the ability to trace and follow a food, feed, food-producing animal or substance intended to be, or expected to be incorporated into a food or feed, through all stages of production, processing and distribution3
References and Resources
1: European Commission; About TRACE; http://www.trace.eu.org/menu/project/
2: European Commission; Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the council of 28 January 2002
3: European Commission; Food Traceability factsheet; http://ec.europa.eu/food/food/foodlaw/
4: US Food and Drug Administration; Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002; http://www.fda.gov/RegulatoryInformation/Legislation/ucm148797.htm
5: AMR Research – now part of Gartner; Traceability in the Food and Beverage Supply Chain; www.gartner.com
TraceFood; Recommendations for Good Traceability Practice in the food industry; http://www.tracefood.org/index.php/GTP
| Tel: | +27 11 543 5800 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.technews.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Technews Publishing (SA Instrumentation & Control) |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved