The nanoclutch – transmission of torque at the molecular level
February 2016
News
A model microscopic system to demonstrate the transmission of torque in the presence of thermal fluctuations – necessary for the creation of a tiny clutch operating at the nanoscale – has been assembled at the University of Bristol as part of an international collaboration.
When driving a car, the clutch mechanically carries the torque produced by the engine to the chassis of the vehicle – a coupling that has long been tested and optimised in such macroscopic machines, giving us highly efficient engines. For microscopic machines, however, developing a clutch which can operate at the nanoscale is much more challenging because at this level different physics need to be considered. Thermal fluctuations play an increasingly dominant role as a device is miniaturised, leading to increased dissipation of energy and the need to develop new design principles.
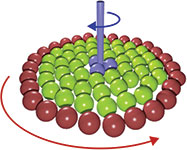
Principle of operation of the nanoclutch: red spheres rotate clockwise and an opposing torque is applied to a central axle.
In the model microscopic system developed by scientists from Bristol, Düsseldorf, Mainz, Princeton and Santa Barbara, a ring of colloidal particles is localised in optical tweezers and automatically translated on a circular path, transferring a rotational motion to an assembly of identical colloids confined to the interior region.
Dr Paddy Royall of the University of Bristol said: “This device looks a lot like a washing machine, but the dimensions are tiny. Through optical manipulation the particle ring can be squeezed at will, altering the coupling between the driven and loaded parts of the assembly and providing a clutch-like operation mode.”
Colloidal suspensions fall into the category of materials known as soft matter and the softness of the rotational device is shown to lead to new transmission phenomena not observed in macroscopic machines. “Exploiting the softness of nanomaterials gives us additional and unprecedented control mechanisms which may be employed when designing microscopic machines,” Dr Royall explained.
In addition to the experiments performed at the University of Bristol, physicists at the University of Düsseldorf have developed model computer simulations to further investigate torque coupling at the nanoscale. This enables the measurement of nanomachine efficiency, which is small but can be optimised through careful control of the system parameters.
The researchers have identified three different transmission regimes: a solid-like scenario which transmits torque much like a macroscopic gear; a liquid-like scenario in which much of the energy input is lost to friction and an intermediate slipping scenario unique to soft materials which combines aspects of the solid-like and liquid-like behaviours.
“A basic understanding of the coupling process will give us insight into the construction of nanomachines, in which torque transfer is absolutely essential,” said Professor Hartmut Loewen of the University of Düsseldorf.
The research is published in Nature Physics.
For more information contact Paddy Royall, University of Bristol, +44 117 928 7668, [email protected]
Further reading:
RS South Africa shapes future engineering talent
RS South Africa
News
RS South Africa is demonstrating that nurturing future engineers goes beyond traditional classrooms or competitions. On STEM Day, the company shone a light on the full spectrum of its educational initiatives.
Read more...
ABB and Compu-Power bring high-efficiency UPS innovation to IS3 X-Change 2025
News
ABB recently participated in the 31st annual IS
3X-Change 2025 in Cape Town, alongside its long-standing channel partner Compu-Power.
Read more...
UKZN’s SMART lab wins aviation award
News
: The SMART Lab at UKZN was awarded first place in the Aviation Research and Development category at the Civil Aviation Authority of South Africa’s award ceremony for outstanding contributions and achievements in the aviation sector.
Read more...
Meta and partners announce completion of 2Africa subsea cable system
News
Meta, in partnership with leading global and regional telecommunications companies, has announced the completion and activation of the core 2Africa subsea cable system. This marks a historic milestone in digital infrastructure, establishing what the world’s longest open-access subsea cable system.
Read more...
RS South Africa retains Level 2 B-BBEE status
RS South Africa
News
RS South Africa has once again achieved Level 2 B-BBEE verification.
Read more...
SEW-EURODRIVE unveils world class facility in Gqeberha
News
In a landmark event in the Eastern Cape attended by key customers and industry leaders, SEW-EURODRIVE officially opened its expanded state-of-the-art facility in Gqeberha, marking a major milestone in its strategy to strengthen regional support and deepen its footprint in the region.
Read more...
Africa’s brightest young battery innovators
Schneider Electric South Africa
News
Schneider Electric and Enactus, the international NGO dedicated to inspiring students through entrepreneurial action, have announced the winners of the 2025 Energy Transition Battery Innovation Challenge, funded by the Schneider Electric Foundation. It empowers young innovators to design battery solutions addressing the region’s most pressing energy challenges.
Read more...
Africa’s strategic role in powering the global clean energy future
News
The 2026 Africa Energy Indaba is to spotlight Africa’s mineral wealth, industrialisation potential and the urgent need for sustainable value chain development.
Read more...
The road to the Indaba
News
The Africa Automation Indaba 2026 is set to become a landmark gathering for Africa’s automation, process control and manufacturing community.
SA Instrumentation and Control will be running a dedicated editorial series spotlighting the voices, ideas and debates shaping Africa’s industrial future.
Read more...
Crash reconstruction tests advance vehicle safety research
News
The University of KwaZulu-Natal’s Scientific Multidisciplinary Advanced Research Technologies (SMART) Lab recently participated in a series of collaborative crash reconstruction tests held at the Toyota Test Track.
Read more...