Paving the way for way for ultra-fast sustainable computers
May 2023
Editor's Choice
Sensors & Transducers
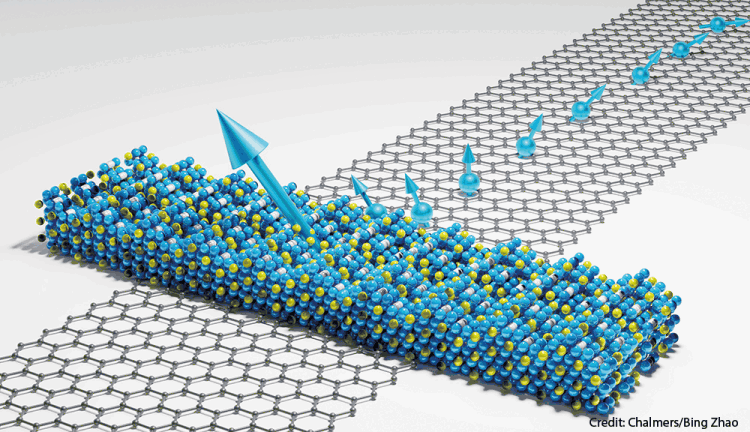
Researchers have for the first time succeeded in demonstrating a device, based on a 2D magnetic material, in room temperature. The 2D magnetic crystal is shown as the blue, yellow, and white balls and is a mix of Iron, Tellurium, and Germanium atoms. The big turquoise arrow indicates the magnetisation direction of the 2D magnet. The crystal with grey colour is the carbon atoms of the graphene channel. The smaller turquoise arrows indicate the spin-polarised electrons injected from the 2D magnet into the graphene channel. Here, the 2D magnet acts as a source for spin-polarised electrons and the graphene channel for spin transport and communication.
The discovery of new quantum materials with magnetic properties are believed to pave the way for ultra-fast and considerably more energy efficient computers and mobile devices. So far, these types of materials have been shown to work only in extremely cold temperatures. Now, a research team at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden is the first to make a device made of a two-dimensional magnetic quantum material work at room temperature.
Today’s rapid IT expansion generates enormous amounts of digital data that needs to be stored, processed and communicated. This comes with an ever-increasing need for energy − projected to consume over 30% of the world’s total energy consumption by 2050. To combat the problem, the research community has entered a new paradigm in materials science. The research and development of two-dimensional quantum materials, that form in sheets and are only a few atoms thick, have opened new doors for sustainable, faster and more energy-efficient data storage and processing in computers and mobiles.
The first atomically thin material to be isolated in a laboratory was graphene, a single atom-thick plane of graphite, that resulted in the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics; and in 2017, two-dimensional materials with magnetic properties were discovered for the first time. Magnets play a fundamental role in our everyday lives, from sensors in our cars and home appliances to computer data storage and memory technologies, and the discovery opened the way for new and more sustainable solutions for a wide range of technology devices.
“Two-dimensional magnetic materials are more sustainable because they are atomically thin and offer unique magnetic properties that make them attractive for developing new energy-efficient and ultra-fast applications for sensors, and advanced magnetic memory and computing concepts. This makes them promising candidates for a range of different technologies”, says Saroj Dash, professor in Quantum Device Physics at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden.
So far, researchers have only been able to demonstrate two-dimensional magnets in extremely low temperatures in laboratory environments, so-called cryogenic temperatures, inhibiting their broader use in society. The researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have been able to demonstrate, for the very first time, a new two-dimensional magnetic material-based device at room temperature. They used an iron-based alloy (Fe5GeTe2) with graphene, which can be used as a source and detector for spin polarised electrons.
Conventional electronic logic devices are based on nonmagnetic semiconductors and use the flow of electric charges to achieve information processing and communication. Spintronic devices, on the other hand, exploit the spin of electrons to generate and control charge currents, and to interconvert electrical and magnetic signals. By combining processing, storage, sensing, and logic within a single integrated platform, spintronics could complement and, in some cases, outperform semiconductor-based electronics, offering advantages in terms of scaling, power consumption, and data processing speed.
The breakthrough is believed to enable a range of technical applications in several industries as well as in our everyday lives. “These 2D magnets can be used to develop ultra-compact, faster, and more energy-efficient memory devices in computers. They may also be used to develop highly sensitive magnetic sensors for a wide range of applications, including biomedical and environmental monitoring, navigation, and communication,” concludes Bing Zhao, post-doctorate researcher in Quantum Device Physics and first author of the study.
Further reading:
Machine health monitoring with ifm
ifm - South Africa
Editor's Choice IT in Manufacturing
With ifm’s machine health monitoring, early signs of wear can be detected and unexpected failures prevented. Combined with equipment preventive maintenance software, interventions can be scheduled proactively to avoid costly downtime.
Read more...
Powering Africa’s sustainable mining
VEGA Controls SA
Editor's Choice Level Measurement & Control
At the 2026 Mining Indaba in Cape Town, one theme rises above all others, progress through precision. For VEGA, a global leader in process instrumentation, this mission aligns perfectly with its core purpose, which is turning measurement into meaningful progress.
Read more...
PCS Global delivers turnkey MCC installation in Botswana
PCS Global
Editor's Choice PLCs, DCSs & Controllers
PCS Global is delivering a turnkey containerised MCC installation for a major copper mining operation in Northwest Botswana.
Read more...
SEW-EURODRIVE transforms drivetrain uptime
SEW-EURODRIVE
Editor's Choice Motion Control & Drives
The DriveRadar IoT Suite from SEW-Eurodrive is an ideal solution for industrial condition monitoring. This powerful ecosystem of intelligent sensors, edge devices and cloud-based analytics ensures that customers have full visibility and control of their operations.
Read more...
PC-based control for flat wire motors for electric vehicles
Beckhoff Automation
Editor's Choice Motion Control & Drives
Special machine manufacturer, ruhlamat Huarui Automation Technologies has unveiled the second generation of its mass production line for flexible stators with bar winding (pins). This enables an extremely short production cycle and line changeover times, supported by PC- and EtherCAT-based control technology from Beckhoff.
Read more...
Heavy impact, smart control
Axiom Hydraulics
Editor's Choice Pneumatics & Hydraulics
Every now and then a project lands on your desk that’s equal parts heavy machinery and fine control - a tantalising mix for any engineer. A client approached Axiom Hydraulics with a project exactly like this.
Read more...
Pneumatics makes a technological leap with the proportional valve terminal
Festo South Africa
Editor's Choice Motion Control & Drives
Festo continually makes bold technological leaps to keep pace with global advancements. Controlled Pneumatics is redefining the boundaries of compressed air technology to meet the demands of today’s most advanced applications.
Read more...
Driving fluid power forward
Editor's Choice News
The National Fluid Power Association is developing its latest Industrial Technology Roadmap for 2025, showing how hydraulics and pneumatics are changing to meet new industrial demands.
Read more...
World’s hottest engine
Editor's Choice Motion Control & Drives
Scientists have built the world’s smallest engine. It’s also the world’s hottest. It could provide an unparalleled understanding of the laws of thermodynamics on a small scale, and provide the foundation for a new, efficient way to compute how proteins fold.
Read more...
PC-based control optimises robotic parts handling on plastics machinery
Beckhoff Automation
Editor's Choice Fieldbus & Industrial Networking
NEO is a cartesian robot developed by INAUTOM Robótica in Portugal for parts removal on plastics machinery. Its aim is to increase system productivity. NAUTOM Robótica has entered into a strategic partnership with Bresimar Automação to increase the working speed of the cartesian robots using advanced control and motion solutions from Beckhoff. The result is a comprehensive, future-proof automation solution for its entire family of cartesian robots.
Read more...

