
The longer I work in the field of control loop optimisation, the more I learn that things often do not work the way one expects. I have spent over 30 years optimising literally thousands of feedback control loops and have gained tremendous confidence and experience. However, I still frequently encounter new and sometimes strange happenings, which need a lot of thought and experimentation to try and understand how to control them in the best possible way. A case in point being when I was recently requested to optimise the main temperature control on a distillation column.
Distillation column dynamics
A portion of the fluid that collects at the bottom of a distillation column is recycled through a steam-heated heat exchanger generally known as a ‘reboiler’. The temperature at the bottom of the column is kept constant by regulating the amount of steam passing through the reboiler. Figure 1 shows a few of the controls normally present on distillation columns.
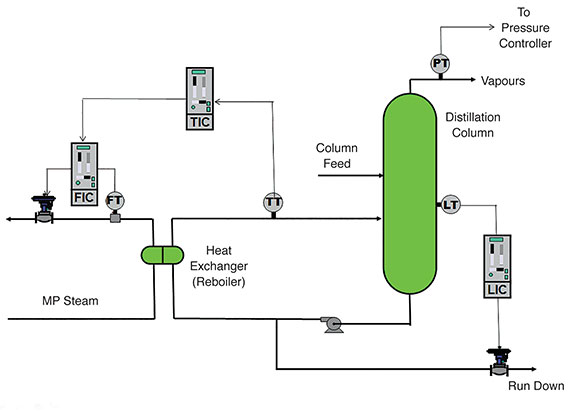
I have in the past optimised the controls on quite a few columns, and generally, the dynamics in a reboiler temperature control process consists of a simple self-regulating process, with a large first order lag and a small deadtime. Like the vast majority of slow temperature controls, it takes time and patience to do the necessary testing for successful tuning of the temperature controller. However, it is not difficult if you have the right analytical and tuning equipment.
This time it was not so straightforward
Figure 2 shows the open loop step test which is used for tuning on such a process. (As one can only make very small changes on the temperature when performing the test, it is necessary to draw a ‘best-fit’ line through the noise of the PV signal to establish the true dynamic constants.)
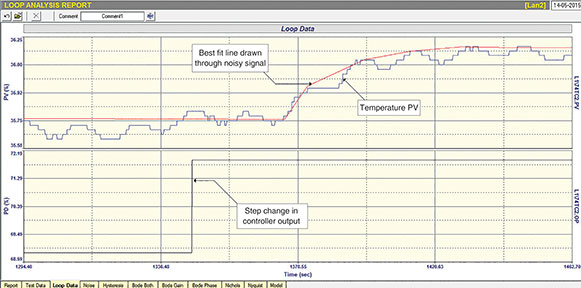
Nearly all the reboiler temperatures I have tuned have worked extremely well after optimisation. However, the one under discussion here proved to be very difficult. Figure 3 shows the open loop test performed on the temperature.
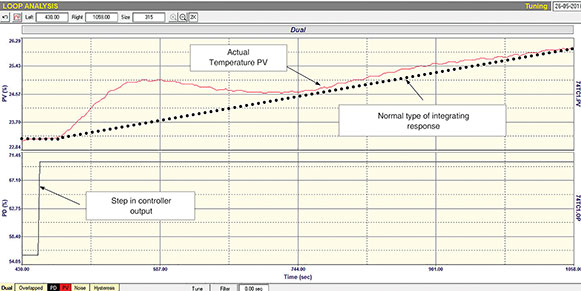
Firstly, for some unknown reason, the process behaved more as an integrator than as self-regulating, and although the test was repeated quite a few times, the temperature just seemed to keep on integrating when a step change was made. This does not make much sense, and I had some in-depth discussion with several experienced process engineers, but nobody has been able to explain why this particular column reacted in this way.
Secondly, immediately the output of the controller was stepped, there was a very fast rise in temperature which eventually slowed down and then came slowly back until the ramping temperature started it moving up again. This is a most unusual response, and we repeated the test many times, and this time trended most of the other controls. It was then found that for some reason the pressure, measured at the top of the column, reacted immediately when the output of the temperature control moved. This again does not make much sense, as the temperature itself has not had time to change under the influence of the change in steam, but the pressure change caused the temperature to ‘jump’ virtually immediately. Again, no one has been able to offer a rational explanation for this.

Tuning as an integrator solves the problem
We finally tuned the temperature as a ‘straight’ integrator as shown by the dotted line in Figure 3. The final tuning worked extremely well. There is definitely some interaction between column pressure and temperature, but it is not serious.
This is not the first time we have come across mysterious and unexpected happenings in the control world for which no rational explanation seems to exist. I would welcome any readers’ comments on this. Possibly someone else has experienced a similar phenomenon?
Michael Brown is a specialist in control loop optimisation with many years of experience in process control instrumentation. His main activities are consulting, and teaching practical control loop analysis and optimisation. He gives training courses which can be held in clients’ plants, where students can have the added benefit of practising on live loops. His work takes him to plants all over South Africa and also to other countries. He can be contacted at Michael Brown Control Engineering cc, +27(0)82 440 7790, [email protected], www.controlloop.co.za
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.controlloop.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Michael Brown Control Engineering |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved