
Stand-alone office PCs are rarely, if ever, suited for the industrial environment, not only in terms of their potential for failure in demanding operating conditions, but also because of the consequences of such failures coupled to labour-intensive and high-maintenance costs in installations of any size.
“Previously, the InTouch scada assets at BASF’s Port Elizabeth Mobile Emissions Catalyst plant were based on stand-alone systems running under-specified PCs,” says Howard Loftus, information management specialist, BASF South Africa. “This presented a high risk of failure because of the lack of redundancy and also a maintenance challenge because these individually managed PCs would all be running different software revisions. So if one failed and was replaced, it wasn’t always with the same software version and this would lead to costly downtime.”
Time for change
BASF set out clear project goals for migrating to a more robust and dependable scada environment. These included:
* Reducing the risk of line stoppages due to system problems thereby also reducing production losses. This is particularly applicable to batch processing because interrupted batches lead to rework and/or scrap at significant cost to the company.
* Minimising hardware failures which, once again, lead to production losses due to the sensitivity of interrupted batch processes.
* Replacing under-specified PCs with hardware rated for industrial use.
* Lowering the total cost of ownership.
“To realise these goals, a system was required that would provide central management of software upgrades and deployment as well as failover capability using appropriately rated computing hardware,” says Loftus. “The new system would have to be introduced without causing production downtime. To help with all this, we appointed Business Connexion Industrial Solutions as our system integration partner who did an evaluation of our existing infrastructure before suggesting a solution based on Terminal Service and ACP ThinManager.”
From an IT point of view, this would address the following:
* Centralised software administration and management.
* Server centric deployment.
* High system speed with minimum network load.
* Improved security.
* Higher system availability.
In addition, ACP-compliant terminal clients meant that no firmware would be required on the terminals which would consist of solid-state, industrialised units with no moving parts.
Implementation
BASF converted their InTouch licences to InTouch for Terminal Server versions and purchased ACP ThinManager (mirrored – ie, master and redundancy configuration). This would provide double redundancy through application and physical layers. The project was to be implemented over two phases. The first (completed at this time of documenting) consisted of:
* Converting the critical applications to the Terminal Server.
* Converting the remaining, less complicated, applications to Terminal Server.
* Implementing critical application redundancy.
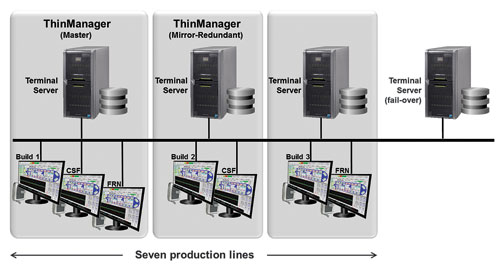
“The critical applications were converted first because these were the source of highest loss in downtime,” says Loftus. “By doing so, we realised an immediate improvement in ROI. The less-critical applications would be easier to resolve. The engineers involved saw their job becoming easier and easier as the critical applications were addressed first.”
Challenges
* Complex InTouch applications with large amounts of hard-coded scripting had to be redeployed in a Terminal Services environment. “Where we previously had a 1:1 ratio where one PC was allocated to each production line, we now have a 4:1 ratio with three clients to one server,” says Loftus. “This meant that data from three production lines were present in the same server but had to be stored in separate data locations.”
* Time constraints for testing due to long batch runs and 24/7 production. Only about half an hour per shift change was available for development and testing in a live environment, there was no off-line simulation.
* Training – getting users to adapt to the client/server topology and architecture.
Business benefits
* Reduced maintenance cost and time – Industrial clients are low on maintenance since failed units are simply replaced by working ones. No configuration is necessary.
* Decrease in production losses – “On two occasions the redundancy server kicked in over a weekend and no one was aware of this until Monday morning. Just these two instances resulted in significant cost saving ,” says Loftus. “There is no doubt that robust client hardware with applications running in a secure server environment is making a difference.”
* Lower cost computer hardware – Previously, PCs that failed because of environmental conditions were repeatedly replaced. “Because of their robust nature, we haven’t yet had to replace a thin client,” comments Loftus.
* Reduced total cost of ownership – This is mainly due to reduced servicing, maintenance and power costs.
Operational benefits
* Reduced downtime which ultimately minimises production losses in a very critical and expensive production process. So far, this has been the largest cost saving.
* Increased security – Centralised deployment of applications, patches and anti-virus software etc. are all done on the servers. Users cannot introduce viruses, worms or other malware through the thin clients because there is no physical way of doing so.
For more information contact Jaco Markwat, Invensys Operations Management, +27 (0)11 607 8100, [email protected], www.iom.invensys.co.za

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved