

From the source to the treatment plant to consumers’ homes we are losing between 15 and 50% of our potable water supply due to leaking pipes in the distribution system. This water loss is a waste of resources a waste of money and a hard hit to the bottom line.
The challenge in the water industry is pervasive due to lack of refined methodology and data, the majority of water companies do not know how much water they are actually losing, and for those who do they do not know where to start fixing the problem. With resource scarcity coupled with consumption and environmental demands, utilities can no longer ignore the problem with a ‘Let it leak’’ attitude.
To pinpoint the exact source of leakage companies need to have a consistent, ongoing and reliable process to automatically collect and then analyse data from fixed or portable meters and district metered areas (DMAs).
Holistic approach
With its merger in August 2007, the Halifax Regional Water Commission (HRWC) is the first regulated water, wastewater and stormwater utility in Canada. It is a fully metered utility providing drinking water to about 325 000 residents of Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM) through a 1300 km pipe network.
The utility has significantly reduced leakage by adoption of the IWA/AWWA best practice methodology and incorporating the collection and advanced analysis of realtime and historical data. The holistic approach is centred on leak detection, pressure management, speed and quality of repairs and asset management.
A major step in implementing the IWA/AWWA methodology was the creation of district metered areas to identify and control water loss, both within each zone and for HRWC as a whole. DMAS enable utilities to know exactly where the water is going and where the leakage is prominent. Once established, a functional DMA can provide the information required to identify unreported leaks and bursts, prioritise problems and direct crews in the most efficient way.
Leak detection and resolution is only as good as the underlying data. Therefore, having an automated solution in place that effectively warehouses billions of data points and offers time-based data is an important component of HRWC’S strategy.
Scada and PLC systems in filtration plants and distribution networks deposit information from more than 60 DMAS into the OSIsoft PI System, an enterprise data historian designed for temporal or time-based data. The PI System stores all plant and distribution information and makes the data accessible to users for analysis or display.
Although intended primarily for water loss control the historical DMA data is routinely used for system design or planning. HRWC engineering staff access the information and view the realtime hydraulic grade line for modelling purposes, while treatment plant personnel use the historical data for demand forecasting and realtime data for water quality compliance. With the PI System HRWC can collect analyse and disseminate necessary data from more than 120 m across its treatment and distribution facilities to determine the period of a leak the amount of leakage and narrow the location to a specific DMA. With this information, the daily net water system input is calculated for each region and posted to the HRWC intranet site for review. Weekly averages are plotted to create an annual trend with previous years overlaid.
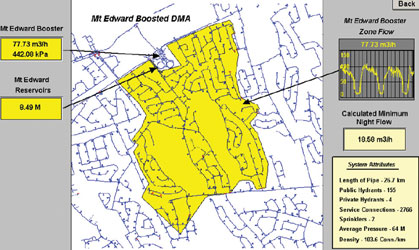
As part of the leakage identification strategy, HRWC has automated its ‘’whiteboard’ – previously a manual process involving posting flow rates on an actual whiteboard. The automated system is based on OSIoft’s Datalink technology, which determines the average flow rate for each DMA between 3 and 4 a.m. then compares these values to established benchmarks for the corresponding DMAS. The results form a table that include the benchmarks of the calculated average night flows for five consecutive nights, and the calculated difference between the benchmark and the most recent night flow. Each morning, the whiteboard for each region, displayed in OSIsoft’s ProcessBook technology, is updated on the HRWC intranet site while printed copies are produced for leak detection personnel.
The whiteboard identifies DMAS with high night flows which can then be analysed in detail to reveal burst times and flow rate. This helps HRWC pinpoint high priority leaks, improving efficiency of resource allocation. The PI System’s graphing tools and long term storage enable staff to review DMA flows over long periods and identify gradual increases in night flows which can indicate an accumulation of multiple small leaks or progression of an unreported burst.
Large customers with sporadic flows can often be mistaken for leakage within a DMA. To prevent this HRWC has partnered with some large customers and installed flow monitoring equipment on-site. Deducting the customer flow from the DMA flow eliminates these false alarms. The scada system monitors and records the flow to the customer through a revenue meter at the inlet to the customer site. HRWC is working toward providing the flow data to customers to allow them to identify their own leaks.
The HRWC has developed a ‘water loss calculator’, a customised Excel application which also relies on OSIsoft’s Datalink technology. Using DMA data from the PI System, the water loss calculator determines the volume of water lost from any abnormal event. Since adopting the IWA Standard Water Balance, the HRWC attempts to accurately measure or quantify, whenever possible, all un-metered water. System flushing, fires, capital work and other maintenance activities are measured using the water loss calculator. All water is accounted for on an annual basis to determine the impact on revenue and success of the utility’s progress.
Water saved, dollars saved
The first North American municipality to adopt international best practices on water loss control in distribution systems, HRWC has revolutionised leakage prevention.
As a result of its adoption of the IWA/AWWA framework and technology integration with the PI System, HRWC has reduced leakage of potable water from its distribution system by almost nine million gallons per day, which represents an Infrastructure Leakage Index (ILI) reduction of 9,0 to 3,0 translating to savings of more than $550 000 per year.
In addition to saving HRWC millions of dollars the automated collection dissemination and analysis of real-time data and subsequent reduced water loss has brought additional benefits to the utility, including:
* Deferral of capital investment and extended equipment lifecycles.
* Reduction in greenhouse gases (as the production and distribution of drinking water is very energy intensive).
* Improved customer buy-in for water conservation due to the utility’s reduction in water waste.
* Decrease in service interruption to customers.
* Decrease in damage to adjacent properties by early detection and repairs under controlled conditions.
* Minimised liability from damage claims as the utility demonstrates a commitment to best practices in water loss control.
* Increased public health protection with elimination of long-term, aggravated leakage.
Data that is visible, accessible and actionable is the foundation for any utility looking to optimise the process as described in the IWA/AWWA framework. With the PI System in place as a proven data historian HRWC is able to facilitate decision making, quickly respond to issues and reduce water loss.
HRWC’s adoption of leakage control strategies promoted by IWA/AWWA can be measured in terms of recaptured water and corresponding value of the water. This economic assessment should influence a utility’s decision to either increase or reduce leak detection activities in a particular zone of the distribution system.
About the author
Carl D. Yates, M.A.SC., P.Eng., is general manager of the Halifax Regional Water Commission. He provides direction for 335 employees within six departments and is responsible for delivery of capital and operating budgets long term planning and development of corporate business strategies. The Halifax Regional Water Commission (HRWC) is the first regulated water, wastewater and stormwater utility in Canada and is located in the Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM). An autonomous, self-financed utility, the HRWC is a fully metered water utility providing drinking water, wastewater, stormwater and fire protection services to about 325 000 residents.
For more information contact Nick Stead, OSIsoft, +27 (0)31 767 2111, [email protected], www.osisoft.com

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved