

One of the greatest challenges in implementing computer systems in a pharmaceutical manufacturing operation is regulatory compliance. This is especially so when the plant is subject to periodic inspection by foreign inspection authorities such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and regulations are in a state of flux.
The change in FDA philosophy initiated in 2003 from a prescriptive paper-trail compliance approach to a risk-assessment based approach has become a driver of regulatory transformation.
FDA changes CFR Title 21
In December 2007 the FDA released a direct final rule that inter alia impacts on the interpretation of FDA CFR Title 21 - Food and Drugs, section 211 requirements for a second individual to check certain activities performed by another.
Various sections of Part 211 require a second person to verify the activities of a first. For instance, section 211.103(d) requires that each component added to a batch by one person must be verified by a second.
Similarly, 211.188(b)(l1) requires that batch production and control records shall include identification of the persons performing and of those directly supervising or checking each significant step in the operation.
The use of computers, related systems and automated equipment appears to make these verifications redundant, but there has been uncertainty in terms of how the use of such systems impacts on current good manufacturing practice (CGMP).
The new direct final rule amends 211.101(c) and (d1), 211.103, 211.182, and 211.188(b)(11) to indicate that the use of automated equipment under 211.68 may eliminate the need for verification by a second individual and that in those situations only one person is needed to verify that the automated equipment is functioning properly.
This amendment may facilitate the introduction of more automated systems into finished pharmaceutical manufacturing. Such systems must comply with the relevant requirements of FDA CFR Title 21 - Food and Drugs - a vast document which cannot be précised in a couple of pages. Specifiers, designers and programmers need to be aware of the regulatory requirements for electronic records and electronic signatures in order to select, procure, manufacture and put into service systems that are 21 CFR compliant.

Electronic records and signatures
The FDA has been involved in setting regulations relating to the use of computerised systems in the pharmaceutical industry since 1978, when they published section 211.68, which provides that automatic, mechanical, or electronic equipment or other types of equipment, including computers, or related systems that will perform a function satisfactorily, may be used in the manufacture, processing, packing, and holding of a drug product, subject to certain requirements.
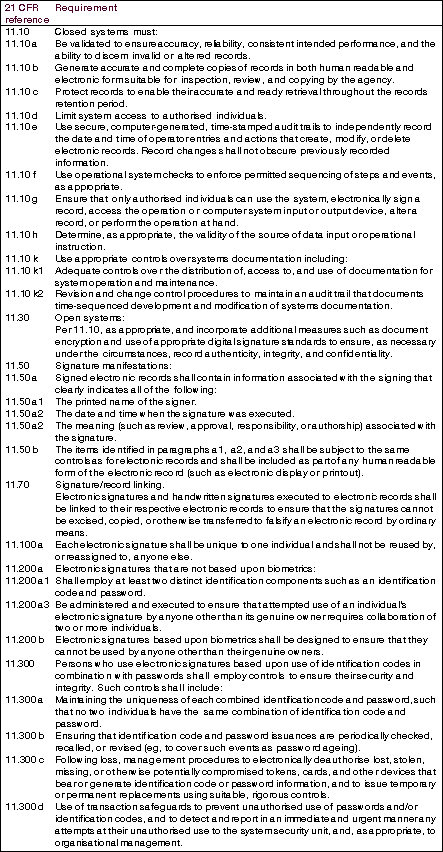
The first draft of 21 CFR Part 11 - Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures (Part 11) was issued in the early 1990s. The final version of Part 11 was issued in March 1997 after considerable public and industry debate. Its intent was to provide a uniform approach that would ensure that in complying with Part 11, manufacturers' paperless record systems would be compliant with CFR 21 parts 210 and 211 CGMP regulations.
Part 11 differentiates between closed systems (Section 11.10) and open systems (Section 11.30) (see Table 2: Definitions) The principal requirements for electronic records, signatures and their controls as they relate to computer software are shown in Table 1: Some requirements for electronic records and signatures. This can be used as a quick reference when specifying, designing or selecting a system where there is intent to operate under FDA 21 CFR. For the complete requirements readers should refer to the full FDA documentation.


Other regulations and guidelines
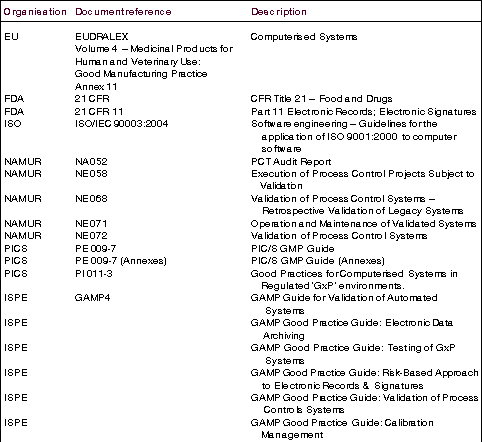
Of course, the FDA is not the be-all and end-all of pharmaceutical manufacturing regulation. The use of computerised systems, control systems and automation in regulated industries is also addressed by such organisations as the European Union, the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering, NAMUR and the Pharmaceutical Inspection Cooperation Scheme amongst others. Quality standards are also covered by the ISO 9000 series, where ISO/IEC 90003:2004 Software engineering - Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001:2000 to computer software has some relevance.
About the author

Andrew Ashton has electrical, mechanical and business qualifications and has been active in automation and process control since the early 1980s. Since 1991 he has headed up a company that has developed formulation management systems for the food, pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing industries and manufacturing solutions involving the integration of various communication technologies and databases. Developed systems address issues around traceability, systems integration, manufacturing efficiency and effectiveness. Andrew is feature editor for SA Instrumentation and Control and editor of Motion Control in southern Africa.
| Tel: | +27 11 543 5800 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.technews.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Technews Publishing (SA Instrumentation & Control) |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved