

To increase their competitiveness, a number of manufacturing companies are starting to incorporate cloud-based Internet of Things (IoT) using simple architectures that extend the existing plant and business systems.
Cloud-based IoT is a potential game changer that allows businesses to extend and further automate their processes using data from lots of sensors outside the factory by leveraging global infrastructures such as Microsoft Azure IoT platform.
A proliferation of choices
However, cloud-based IoT currently resembles the Wild West with multiple startups and established vendors alike competing for a role in this fast growing market.
The IoT is fundamentally comprised of devices that connect and interact with one another through the Internet and there are no limits to how this can be done. The devices can range from simple microprocessors like Arduino, to sophisticated smartphones or tablets.
Certain industrial applications are well-suited to cloud IoT. For example, fleet management, predictive maintenance, asset management, logistics, warehouse and facilities monitoring services. These applications augment and enhance your existing manufacturing processes. Unlike process control, they don’t need to have a permanent connection, and asynchronous offline operation is entirely feasible. When the device or connection fails, the system degrades in a way that should be easy to handle.
Keep it simple
When considering a cloud IoT application it is helpful to start with a simple architecture like that shown in Figure 1. This will allow you to selectively research and invest in specific platforms that will ultimately form part of your IoT infrastructure. In this way you can start with a proof of concept and with experience move towards more mission critical applications.
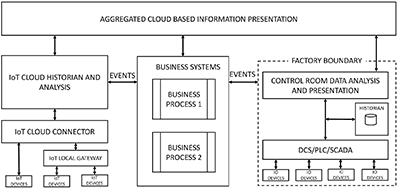
Figure 1 shows your existing process control system within the factory boundary at the bottom right. In the middle are your business systems (ERP and so on); and on the left your new cloud IoT services. These three high level architectural elements are connected by events that communicate processed information. The information that is produced is aggregated and further analysed in a presentation layer, also hosted in the cloud.
Connection to the cloud
In order to accommodate the increasing diversity of IoT devices you will need to accommodate various means of connection to the cloud. Certain devices can be connected directly, others will require some form of local gateway that converts the various communication protocols from the devices to a standard, and might also provides some form of security. All IoT devices will ultimately connect to a IoT cloud connector service that authenticates the hardware and establishes communication using relevant protocols. Note that the communication is bidirectional and not all devices will have offline asynchronous capabilities. This introduces several real-world complexities.
The IoT cloud connector in turn feeds the pre-processed data streams to the IoT cloud historian and analysis layer. Here the data is cleaned and analysed into calculated variables that might trigger events. There is no real use in collecting data that does not ultimately result in some action being taken that leads to a business outcome. What is important is that these events are properly handled in your business processes. This might require some re-engineering of your processes to incorporate these new events from the IoT cloud. An example might be a remote device triggering a fault after which a regionally located technician is automatically allocated to do some maintenance. Your architecture should also incorporate some form of cloud-based historian which will allow proper trending and analysis to be done, in very much the same way as your local scada historian at the factory is most likely currently used.
At the top, the cloud-based presentation layer will present end-users with user-friendly dashboards and tools to interpret the information and to track processes. This architectural element may incorporate cloud-based technologies from your business systems and even your factory systems. Here it is important to try and provide a unified end-user experience that incorporates the total process.
Choosing the platform
Other considerations when considering cloud-based IoT architectures are scalability, reliability, security and privacy. A very real consideration is how to automate the upgrade and deployment of future patches to potentially thousands of devices and associated micro services, without ‘breaking’ the system entirely. These are very real challenges that are addressed in different ways by the major cloud IoT platform vendors and are certainly worthy of further investigation before committing.
At a very high level it is a good idea to view the cloud IoT architecture as augmenting and running in parallel with your core business and manufacturing system. The reality is that you will be doing a lot of experimenting and proof of concept work until the underlying technologies have matured and the platforms have stabilised. While much of the system will be in your control, you will nevertheless be reliant on multiple third-parties, including software and hardware vendors. When designing the final architecture, always strive to ‘fail safe’. In other words, when the IoT device sends garbage data it should be possible to ignore this and continue to operate, albeit less efficiently.
At the end of the day, because of the moving landscape, it is difficult to design for a cloud IoT system. It is a really good idea to get started with some sample applications and develop your own connected application to build experience. There are several cloud-based systems that will allow you to do this, for example, ThingSpeak.com, myDevices.com and the Microsoft Azure IoT platform, each with vastly different capabilities. There are many others. Develop non-critical applications first and be willing to abandon these when things change. As you succeed the business should start recognising the potential value of this approach and be more willing to advance funds towards larger more critical projects.

Gavin Halse is a chemical process engineer who has been involved in the manufacturing sector since mid-1980. He founded a software business in 1999 which grew to develop specialised applications for mining, energy and process manufacturing in several countries. Gavin is most interested in the effective use of IT in industrial environments and now consults part time to manufacturing and software companies around the effective use of IT to achieve business results.
For more information contact Gavin Halse, Absolute Perspectives, +27 (0)83 274 7180, [email protected], www.absoluteperspectives.com

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved