
An operation the size of Exxaro’s Grootegeluk coal mine depends on accurate and timely contextualised plant-level information. With the necessary expansion of the processing plant to supply the new Medupi power station, traditional manual methods and spreadsheets could no longer cope and Exxaro looked for a solution that would give them the necessary reporting for effective decision support.
Background
With the construction of two new world-class beneficiation plants (GG7 and GG8), Exxaro’s Grootegeluk Medupi Expansion Project (GMEP) will, in terms of an agreement with Eskom, supply the Medupi power station with an average of 14,6 Mtpa of power station coal over the next 40 years. Both plants are dedicated to meeting this considerable production schedule.
On completion of the expansion project, Grootegeluk will be the largest coal beneficiation complex in the world, producing some 33 Mtpa of power station, coking and steam coal.
Grootegeluk’s production reporting was historically and traditionally an Excel-based system which involved manual data capturing onto a number of spreadsheets. From there a series of links and macros did a number of calculations and aggregations which were passed onto more spreadsheets which were then collated to generate reports.
It’s no wonder that the project mandate was simply: “Replace this Excel reporting system.” But any new system would have to meet an extensive list of requirements including:
* Automatic data extraction from plant PLCs – this would include levels and information from belt scale counters, flowmeters, etc.
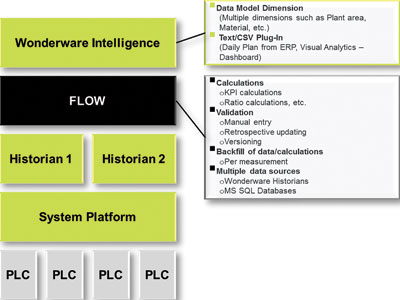
* Calculation and aggregation engine – the engine would have to be configurable with respect to calculations as well as time intervals over which the reports would be based. Examples of information that could be included in reports are KPIs, production ratios and even raw values.
* Validation of data – a key requirement was that data needed to be validated before consideration for use in reports. So manually collected data (e.g. scaling factors or readings from instruments not connected to the PLCs) would have to be checked for validity. In addition, provision was to be made for the retrospective updating of data – for example, in the event of an instrument malfunction or absence for maintenance purposes, its incorrect readings would have to be overridden manually. Once manual data entry is involved, it’s important to introduce a level of version control and change control logging.
* ‘Back filling – it was necessary to leverage the historical data in the existing systems to bring the information up to date.
* Static and dynamic reporting – static reports were those reports that managers could take into meetings, for example. Whereas dynamic reports are analytical and interactive in nature and performed from a laptop or PC.
Implementation
Exxaro selected Wonderware-endorsed system integrator Advansys for the project because the company has manufacturing systems experts and, more to the point for this project, business intelligence specialists.
“The FLOW product provides all the necessary calculations, validation, backfill and connection to multiple data sources,” says Advansys director, Graeme Welton. “Wonderware Intelligence provides a dimensioned data model. For example we can reference plant area, material, planned or actual production values and any number of other dimensions. It also has a CSV plug-in which we use to download the daily plan from the mine planning system. But most importantly, it has dashboard-based visual analytical tools which will help personnel design their own reporting dashboards.”
Wonderware Historian
The Historian is a high speed, high resolution (i.e. < 1 second) and high performance data-logger and database that gathers data from sensors, meters and transmitters.
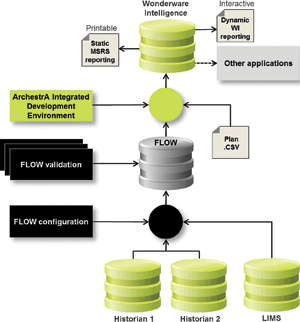
FLOW
This is a configuration-driven reporting solution that integrates into and extends the Wonderware suite (in this case Historian and Intelligence) to provide:
* Calendar definition, allowing creation of ‘time buckets’ (e.g. define different shift patterns).
* A data aggregation and calculation engine.
* Connection to multiple data sources.
* A drag-and-drop configuration environment.
* Data validation, manual entry and retrospective updating.
Wonderware Intelligence
Wonderware Intelligence is a ‘real-time’ data warehousing solution (dimensions and measurements). It comprises two distinct components: the first is concerned with data collection and organisation into a dimensioned model and the second is an interactive visualisation and dashboard tool.
“The Intelligence Analytics Client is essentially the authoring tool for dashboard visualisation. But it’s more than that: it is a self-service analytical tool that is so powerful that I believe everyone should have it on their desktop. Throw away spreadsheets and put this on your desktop – it’s incredible!” says Welton. “Visual analytics and dashboarding are extremely effective management tools because everyone is looking at the same version of the truth drawn from a single data warehouse. The interactive and visual nature of these dashboards significantly increases the speed and confidence of decision making. This functionality will be exploited in future by connecting Wonderware Intelligence to other data sources such as the Wonderware Performance solution. Reports can also be made available on mobile devices if required.”
Benefits
* Greatly improved speed and confidence of near-real-time decision making.
* Single version of the truth.
* Replaced Excel as a reporting solution.
* Independence and ease of use as users can configure their own reports and dashboards – solution is also now used outside of GMEP in most of the Grootegeluk plant.
* Collation of data from multiple sources to provide a cohesive and contextual view of production.
* ‘Back fill’ capability leverages existing Historian data allowing back-tracking as far as needed.
* Validation of all data and the ability to go back in time to correct invalid or missing manual or automatically-derived data.
What’s next?
The success of this project could mean that it will be expanded into the greater Grootegeluk plant. “It can possibly be used beyond production reporting in other areas such as finance or legal compliance with respect to safety and incident reporting,” Welton says “Anything that is time-based and can be attached to a dimension inside Wonderware Intelligence can be reported with this system.”
The next step is to consider Tier 2 which would entail replicating this solution at different mines and processing plants and being able to aggregate all or part of that information for head office to create a divisional reporting solution.
For more information contact Jaco Markwat, Invensys Operations Management Southern Africa, +27 (0)11 607 8100, tech@invensys.co.za, www.iom.invensys.co.za

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved