
Traditionally, pH sensors require replacement and are sometimes seen as consumables due to the frequency of change-out in certain applications. Therefore, suppliers are constantly working on developments to extend the useful lifespan of these sensors using technological advances in materials, and innovative solutions and designs.
In recent years, Foxboro has focused on four factors that influence the useful lifespan of a pH sensor:
• Wetted parts and connections.
• pH glass electrode.
• Silver ion migration (fouling).
• Electrode and reference junction.
In addition to the various fittings and connections with inert parts that facilitate installation, removal, cleaning and calibration.
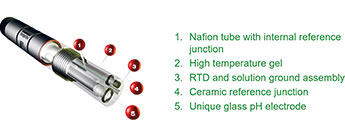
Figure 1 shows the construction that enables the DolpHin sensor’s ability to last much longer in process applications. References exist of increase in operational life from two to three weeks to up to six months in certain applications.
Wetted parts
The DolpHin range of pH sensors consist of a PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride, commercially known as Kynar) body with no metallic wetted parts. Foxboro has developed a unique glass formulation for the electrode and a ceramic reference junction to assist with the accuracy of measurement across the temperature range. Eliminating the metallic wetted parts with the Kynar plastic extends the lifespan of the sensors in corrosive environments such as oleum applications.
Temperature
The use of Kynar as the construction material has allowed Foxboro to develop a unique electrode using a glass formulation allowing the DolpHin pH sensor to be used in higher temperature application up to 120 degrees Celsius. To ensure the accuracy of the electrode under these elevated temperatures, Foxboro has developed a high temperature gel capable of reducing the changes in dissociation constants of the ions in the solution being measured and the glass electrode resistance.
Effect of silver ion migration
Although the pH glass measuring electrode responds very selectively to hydrogen ions, there is a small interference caused by similar ions such as lithium, silver and potassium. The amount of this interference decreases with increasing ion size. Silver ions present the most significant interference. In order to reduce the interference of migrating silver ions in the sensor, Foxboro has developed a Nafion tube that contains an ion barrier. This barrier (a composite silver and potassium compound) inhibits the silver ion migration between the electrode and reference junction – see Figure 2.
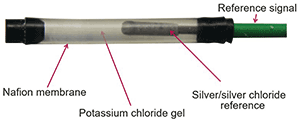
Electrode and reference junction
A pH electrode assembly, or sensor, consists of two primary parts: the measuring electrode is sometimes called the glass electrode, and the reference junction. A galvanic potential is formed when charge exchanges occur at the phase boundaries of the glass measuring electrode. In effect, the pH sensor assembly forms a galvanic cell using two metal conductors and the media. The closer these two parts can be to each other, the more accurate the pH reading.
By using a ceramic reference junction and glass electrode, in conjunction with high temperature gel and Nafion barrier, Foxboro has been able to reduce the gap between the electrode and junction in order to provide a more accurate reading. The factors mentioned above allow the DolpHin sensors to function longer in process environments.
Transmitters
Foxboro has invested significant resources into modernising and developing the functionality of its transmitters. These include:
• Option of dual output with a single transmitter – including pH and ORP concurrently.
• Configuration profiles: two unique profiles can be saved in a transmitter, which allows for reduced spares holding.
• Sensor and transmitter diagnostics.
• Optional USB patch cord connects sensor to PC.
• Device Type Manager (DTM) Software is Field Device Tool (FDT) Group certified.
• Sensor can be calibrated and its history log read and saved to a file.
• Simplifies sensor calibration and diagnostic checking.
Correct maintenance and care procedures
While Foxboro and the other suppliers are making significant advances in the longevity and ease-of-use of the pH sensors, it is vital that the supplier recommendations with respect to maintenance, cleaning, connection and storage of these sensors is followed to ensure that you do get the longest possible use out of your equipment.
For more information contact Gary Bantich, EOH, +27 (0)87 803 9767, [email protected], www.eoh-pas.co.za

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved