
Data is easily collected and stored, but in most cases the data pipeline stops here and there is hardly any value extracted from the data. The data pipeline is often not completed in a proper way so that the right person(s) can easily exploit the value inside the data. It is a challenge to extract the value from the huge stream of data and not to drown in the flood. Simply collecting and storing data is not enough to monetise any investments in Industry 4.0 and IIoT infrastructure.
Getting the maximum value out of the data and keeping an overview of data streams goes beyond standard statistical methods and tooling. Manual analysis and creation of dashboards and reports are not sufficient. The dashboards become too complicated and often do not show the right information at the right time, in the right way, to be able to see at a glance what is going on and be able to act. The routines implemented in a normal machine controller to observe the production process and to detect errors can detect present deviations and problems, but are not suitable to predict future problems. Machine controllers are not suitable to combine all available information and to perform advanced analytics on it.
IT vs OT
Most organisations understand the roles and functions of Information Technology (IT), but in the context of its relationship to Operational Technology (OT), it is probably worth expanding. In simple business terms, IT refers to the application of network, storage, and compute resources toward the generation, management, storage, and delivery of data throughout and between organisations.
Compared with IT, OT is unique in that related hardware and software is historically designed to do specific things, i.e., control heat, monitor mechanical performance, and trigger emergency shutoffs, to name a few. Typically, this is done through industrial control systems (ICS) and supervisory control and data acquisition (scada).
While IT and OT have historically made up separate aspects of modern organisations, a phenomenon known as IT-OT convergence is changing this. Since IIoT technology takes assets not typically connected to the Internet – such as assembly line machinery – and bringing them online, enterprises now have the opportunity to create new efficiencies by applying the intelligence of IT to the physical assets of OT systems.
Transforming data into information
The valuable information needs to be extracted from the data and presented to the right audience, at the right time, and in the right way. The key is to put enough effort into the transformation process of the data into useful information, which should be done in close collaboration between data scientists, who know how to tame the data, and domain experts of the manufacturing process, who know the story behind the data. Once data is transformed into information, a solution can be developed that brings value in the long run.
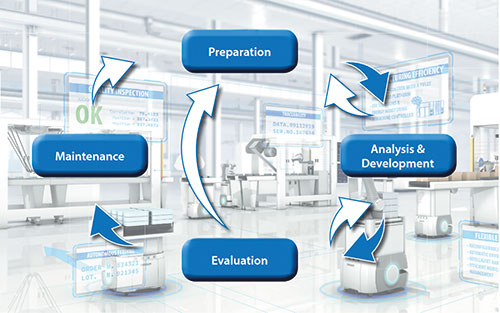
Industrial Data Science is a fairly new discipline and there is no one-size-fits-all solution as of yet. Each solution and application needs tailored data analysis and modelling to obtain the maximum result. Data scientists at Omron follow a standard approach to obtain the best project results and to manage the expectations. The approach is based on the CRISP-DM model. CRISP-DM is the acronym for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining and is widely used.
It is challenging to use the potential of big data. Just collecting it and displaying some graphs is not sufficient. The valuable information needs to be extracted from the data and presented to the right audience, at the right time and in the right way.
| Tel: | +27 11 579 2600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.industrial.omron.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Omron Electronics |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved