
The intention of this paper is to outline the basic requirements for designing and manufacturing an IS mobile device. What are the risks and what do the standards say? This will explain why IS mobile devices are more expensive than standard rugged devices. I have selected five areas where the requirements of IS are important and substantial in order to avoid ignition. All references are to SANS 60079-11:2012 (based on IEC 60079-11:2011), unless otherwise stated. Note that IEC 60079-11:2023 has recently been released and SANS will follow in time.
1) The battery itself is the largest risk. Key issues are battery design, short circuits, overheating, how the battery is charged and battery charge connectivity (USB and magnetic charge terminals). Battery construction is defined in SANS/IEC60079-11, and extensive destructive tests are required (spark ignition, temperature, etc.). SANS/IEC60079-11 6.2.5 defines the requirements for battery segregation and charging. Even if charging is carried out in a non-hazardous area, the charging/data connection must ensure the ratings of protective components are not exceeded. Therefore, the charging connections should either be rated to Um 250 V, or a special charger or cable must be provided. Where the battery is user-replaceable, the IS mobile device should be marked accordingly. External contacts for charging have their own requirements. The standard defines requirements for plug and socket design to prevent accidental and unsafe connection errors.
2) Electrostatic discharges are a source of ignition − some plastics can even be statically charged when wiped or cleaned with a cloth. Aluminium can rust, becoming a spark risk. SANS/IEC60079-0 defines requirements for non-metallic enclosures and for preventing electrostatic charges. SANS/IEC60079-0 also defines requirements for metallic enclosures, with different requirements for Group I, II and III respectively. For example, Group I has a limit of 15% aluminium for use in fiery mines.
3) For accessories that are not purpose-built (scanners, headsets etc., where the accessory Ui Ii Pi must be compatible with the mobile device Uo Io Po), cable connectivity to devices is limited to the Safe Area, and these terminals need either electrical or mechanical protection whilst in use in the hazardous area, to prevent short circuits or sparks. Connectivity points on the device require protection. The magnetic coupling terminals require IP30 (Group II, protected from tools and wires greater than 2,5 millimetres) or IS limiting circuitry to prevent sparks should they be accidentally short-circuited.
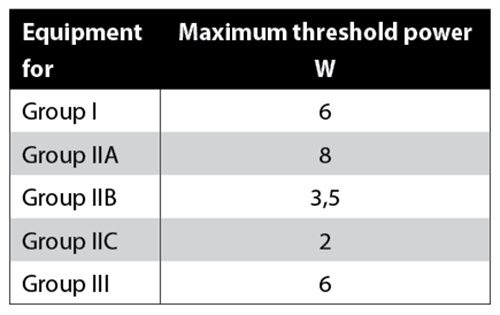
4) RF power needs to be controlled, depending on the hazardous area environment, to avoid induced currents. Whilst Wi-Fi and Bluetooth do not get near the 2 W limit, devices can exceed this with GSM and LTE/4G/5G. RF power should not be user/software configurable.
5) Product design needs to meet safety component power derating, segregation distances, capacitance and inductance, and prevent hotspots. Safety components (resistors, Zener diodes etc.) require 2/3 power derating (a safety factor of 1,5 is required for Exia and Exib). Creepage and clearance (including use of encapsulation) for PCB layout distances (components and tracks) are defined in the standard. There are also requirements to prevent incorrect connection or interchangeability. Fuses must be rated for the Um voltage and be encapsulated.
As can be seen, the requirements for making a device IS are onerous, time-consuming and costly, requiring specific battery design and PCB component level changes to meet power deratings, creepage and clearance. This makes it very difficult and complicated to convert a standard device to Ex ia/ib. Even Ex ic is challenging.
There are also a few practical things to consider when selecting devices. For example there have been reports in Europe of fake ATEX certificates and unsafe devices being issued with ‘legitimate’ ATEX certificates in recent months, as described in https://ec.europa.eu/safety-gate-alerts/. The mechanism for removing non-compliant ATEX devices or certificated devices is fractured, as it is down to the market surveillance authority in each country. There is, however, a formal mechanism for those authorities to collaborate and share information. Other considerations are:
1) IECEx has a mechanism for devices and certificates to be reported and removed. IECEx also has an online database of certificates, so it is easy to confirm certification and validity.
2) Batteries typically have a limited life and typically only a six-month warranty. Devices with replaceable batteries will extend the usable life considerably.
3) MDM compatibility and Android Enterprise compliance provide some guarantee of security and quality.
4) The impact of security with respect to support and bug fixes should be considered.
To read the full article with all the details visit http://www.instrumentation.co.za/*extech.
| Tel: | +27 10 055 7300/1 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.extech.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Extech Safety Systems |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved