
The vortex shedding flowmeter emerged 25 to 30 years ago and has steadily grown in acceptance to become a major flow measurement technique. Its appeal is due, in part, to the fact that it has no moving parts, yet produces a frequency output that varies linearly with flowrate over a wide range of Reynold’s numbers. The vortex meter has a very simple construction, provides accuracy (1% or better) comparable to higher price and/or more maintenance intensive techniques, and works equally well on liquids and gases. It is driven primarily by the fluid and lends itself more readily than other linear flow devices to two-wire operation. Comparing the vortex shedding flowmeter to an orifice plate the former has higher accuracy and rangeability, does not require complex pressure impulse lines, is less sensitive to wear and, for volumetric flow measurement, does not require the need to compensate for fluid density.
General criteria for instrument selection
Instrumentation procurement should include the following criteria when selecting the best fit for the organisation’s requirements:
Price/performance
Meeting performance specifications at the lowest cost is important in any industry. Producers must keep operating costs low to survive. Although compliance with well-honed standards has placed leading vendors at near parity in baseline performance, vendors are constantly innovating to improve accuracy and reliability of their instruments. In this market, the highest priced products are not necessarily the best performing, so careful attention to required functionality and price can pay off. Technology advances make it more feasible to measure multiple variables with a single instrument, which can contribute further purchasing economies.
Warranties
An often overlooked criterion, warranty periods can play a large influence in total cost of ownership calculations. A slightly more expensive initial procurement cost can be significantly offset with longer warranty periods. Additionally, the longer warranty period instils a confidence in the instrument performance for a given time span.
Ease of implementation
Ease of implementation and operation affects both performance and cost of running operations. The less complicated it is to install, configure and use the equipment, the shorter the learning curve is. Ease of implementation includes mechanical design features that impact installation, as well as ease of configuration and calibration.
Maintainability
Maintenance is one of the most significant factors contributing to cost of operations. Contributing to reduced maintenance costs are advances in design, materials, and diagnostics. Proper selection of instrumentation is critical to the overall production and success of the plant. Instrumentation that needs continuous maintenance, such as calibration and repair, or replacement can cause production downtime, thus reducing plant yield. Conversely, instrumentation that requires little maintenance time will boost plant production, while reducing replacement and labour costs.
Flexibility
Flexibility is significant because of the rate at which the market changes, meaning organisations need to be able to obtain the maximum possible use from each sensor they purchase. Careful consideration of these options during the design phase can save thousands by
eliminating the need to purchase individual sensors for different variables and can improve operations by providing process engineers greater flexibility in deploying or repurposing sensors.
Scalability
Closely related to flexibility, organisations want to be sure that the systems they install today can grow with them as their businesses expand. This is primarily a consideration for the control system that is installed, as it must include an open architecture that will enable deployment of best of breed devices, but is also a function of the communications protocol used within the instrumentation.
Support
Availability of support is critical in industry, combined with technology advances that can result in savings of thousands of Rands, but can also add unnecessary costs if implemented without a clear understanding of the process needs of clients and the workings and benefits of latest technological advances. Helping organisations meet these requirements are several trends in sensor design and development, expanded functionality, user access and integration, and vendor support.
Vortex meter application suitability for steam measurement
Vortex flowmeters are well suited to clean liquids and gasses. This makes them ideal instruments in the measurement of steam flows (See Table 1).
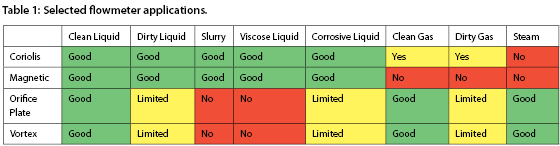
Orifice plates can cost less than other solutions, which makes them very popular. Use of a differential pressure orifice plate requires consideration of pressure loss in the process and calibration of the plate. This kind of device often needs specific software and expertise for setup. In addition, orifice plates can be more susceptible to mechanical wear, resulting in inaccuracies in flow measurement due to increasing hole diameter. In addition, the vortex flowmeter is capable of measuring lower flow ranges.
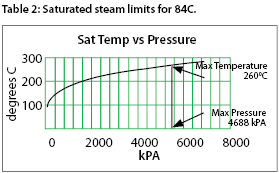
Foxboro’s 84C vortex flowmeter already has the temperature RTD inserted into the thermal well of the flow chamber. Additionally, the mass flow calculator is integrated into the instrument’s electronics with the requisite density corrections and mass calculations. Measurement tolerances are approximately 0,50C and 1% of volumetric flow for liquids and gasses. This equates to a 1,4% accuracy for steam mass flow.
The operating ranges for the 84C (see Table 2) allow operation in most temperature and steam ranges for saturated steam.
For more information contact Gary Bantich, EOH, +27 (0)87 803 9767, [email protected], www.eoh-pas.co.za

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved