

After time, temperature is the second most measured physical unit in production – as well as in quality control and maintenance.
Temperature represents an important indicator of product quality, safety and equipment conditions. Knowledge of the advantages and the limitations of this technology is needed if the correct infrared thermometer for the application is to be selected. It is also helpful to know the principal of operation of infrared thermometers.
During the last five years the IR sensor market has seen two major trends:
Affordability
IR thermometers are significantly lower in cost. The most expensive part of an IR thermometer is the lens and detector. New lens materials and technologies (plastic, Fresnel lenses) and mass production of IR detectors have resulted in lower prices. Together, with the increased demand for industrial IR thermometers, high volume production of standard sensors has resulted in greater manufacturing efficiency for the IR thermometer manufacturers. Some types of IR sensors are up to 50% lower in cost than they were five years ago.
Miniaturisation
IR sensors are becoming smaller in size. In the past, the measurement of low temperatures made it necessary to use fast lenses with relatively large diameters in order to capture enough emitted energy. Progress in detector technology has helped reduce the dimensions of the IR sensing head dramatically. Because the newer sensors exhibit greater sensitivity they require less input energy to produce a usable output signal. As a result, lenses can have smaller diameters. The diameter of a lens may be only a few millimetres, but the sensor has a temperature resolution as fine as 0,1°C, and can measure down to -40°C.
The advantages of IR thermometers are:
* Fast response time (millisecond range), user gets more information per time period.
* Measure the temperature of objects that are moving, rotating or vibrating.
* Measure high temperatures up to 3000°C. (Contact probes will not work or have a short lifetime at high temperatures.)
* No mechanical damage or contamination of the surface (painted surfaces, food, and soft plastics).
* Measure actual product being manufactured instead of another part of the process or inferred measurement.
IR thermometers have special requirements:
* Must have direct line-of-sight.
* The optics of IR thermometers need to be protected against dust or condensation (a variety of accessories are available).
* In general, IR thermometers measure only surface temperatures and the ability to emit thermal radiation depends on the kind of material and especially on the surface finish.
Choice of IR unit
The operating wavelength of the instrument must coincide with that of the application in order for reliable, accurate measurement. It is best to use the shortest possible wavelength for the temperature range and Figure 1 indicates the common wavelengths used with respect to target temperature and error. From this it can be seen that to measure above 900°C one would not use the common 8-14 μm instrument, but rather one having a sensor rated for 1 or 2 μm wavelength.
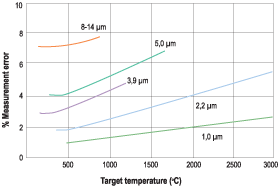
These factors are important when choosing the correct IR thermometer. Note that there are many units on the market that quote low error on high temperatures and have the wrong wavelength detector. (For example, a range of -50 to 1500°C with a 8–14 μm wavelength.)
Advances in IR thermometer electronic design
Process industries continue to need sensors with higher accuracy and repeatability as they look for ways to cut costs, maximise their production lines, and monitor quality. Easy installation, use, and maintenance continue to be important, as does the ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Field checking and field calibration features are becoming more and more important as companies look to optimise their personnel and equipment resources. Manufacturers need IR sensors with a wide operating temperature range that covers more applications and eliminates the demand for water/air-cooled housing, which keeps the cost down due to less water/air consumption and hardware required.
Advances to detectors and optics of infrared thermometers are helping manufacturers and their customers expand the types of applications where IR can be used effectively, gain speed and accuracy, and get a better return on their investments. Two-colour or ratio measurement and units with built-in visual cameras are some of the recent advances.
Raytek and Ircon, suppliers in the infrared measurement industry, design, manufacture, and market a complete line of online and portable noncontact thermometers (IS units included) and line scanners for industrial, maintenance, and quality control applications.
R&C Instrumentation is offering a simple handbook which explains the principles and types of measurement. The handbook covers important factors like different frequencies for different temperatures and single and two colour (ratio) operations. (For a free copy of this handbook e-mail R&C Instrumentation at the address below.)
| Tel: | +27 11 608 1551 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.randci.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about R&C Instrumentation |
© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved